Functions defined by interfaces can also be called “empty body functions”, because only inputs and outputs and no function bodies are specified within MOSAICmodeling. They can be used as placeholders in equation systems. The output and input variables must be defined via an interface, but the mathematical expression will not be specified at that point. In this way, the equation system is independent of the functional correlation used to calculate the output variable. Similar to functions with defined bodies, several variable inputs are possible while only one output variable is calculated. Both input and output variables can be scalars or vectors. Hence, more than one functional dependence can be expressed by the use of one empty body function.
Model description
In this exercise the use of functions defined by interfaces is practiced. The following equation must hold:
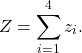
The components ![]() of the vector
of the vector ![]() are calculated via the following mathematical operations:
are calculated via the following mathematical operations:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \begin{align*}&z_1 = x + y \\[2ex]&z_2 = x - y \\[2ex]&z_3 = \frac{x}{y} \\[2ex]&z_4 = x \cdot y. \\[2ex]\end{align*}](https://mosaic-modeling.de/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-18351c2667be385bea031ee27481c3ef_l3.png)
This shall be achieved with an empty body function. The mathemical expressions shall thus be added later, in this case in Matlab. The function’s output variable ![]() is thus a vector. In the simulation,
is thus a vector. In the simulation, ![]() shall be determined iteratively for a given
shall be determined iteratively for a given ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Workflow
Notation of equation system
Set up a notation with the following base names and indices:
Base names
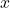 , constant
, constant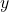 , iteration variable
, iteration variable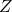 , sum of all components of
, sum of all components of 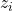
 , vector
, vector
Indices
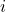 , index for components of
, index for components of  1…NI
1…NI
The resulting notation has ID 182679.
Equations
Now formulate the model equation defined above. The resulting equation has ID 182680.
Definition of interface
To create the interface, do the following in the Interface tab:
- Load the notation
- Add an informative description of the interface
- Add fields for
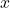 ,
, 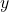 , and
, and 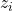 by clicking on “+ Field Name”
by clicking on “+ Field Name” - Select the dimensions of these three variables – Scalar for
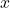 and
and 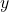 , and Vector for
, and Vector for 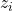
- Select “In” for
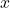 and
and 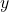 , and “Out” for
, and “Out” for 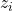 in the In/Out column
in the In/Out column - Go to the Pattern Assistance tab and select Function in General within the Type of Interface
- Save the interface
This interface is available in MOSAICmodeling with ID 182681.
Definition of function
To create the empty body function, we take the following steps in the Function tab:
- Load the notation of this example
- Add an informative description of the function
- Make sure that Load interface is selected in the Interface & Body Settings
- Load the interface you created
- Save the function
The function has ID 182682.
Equation system
Go to the tab Equation System and add your equation in the same way as in the previous examples. Then go to the Functions tab within the equation system and take the following steps:
- Add the function by clicking on the “Add” button at the bottom
- Add an application by clicking on “Add Application”
- Add
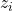 as Applied Naming for the output and
as Applied Naming for the output and 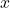 as well as
as well as 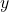 as Applied Naming for the input
as Applied Naming for the input - Confirm that and confirm again to close the popup windows. You should now see one application of the function within the equation system
The resulting equation system has ID 182683.
Evaluation / Simulation
Next, we can move to the “Simulation” section and load the equation system we just created. Then, we take the following steps:
- Add a description for your simulation
- In the tab on the Generic System, go to Functions and check whether MOSAICmodeling confirms one usage of the function in one application
- Go to Indexing and enter 4 as Max Value for NI; then click on Confirm Index Data
- Go to the Specifications tab and assign
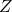 and
and 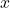 as design values
as design values - The variables
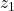 through
through 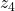 should be classified as calculated values
should be classified as calculated values
Initialization, filling out the the empty body, and results
To initialize and specify the model, take the following steps:
- Initialize this example with the design values and initial guesses given in Table 1
- Save the variable specification
- Save the simulation
- Go to the Evaluation tab and generate the code for Matlab
- Copy the generated code into Matlab and search for the following code:
function[std_z_i] = fun_182682__03_function_emptybody(std_x,std_y)
std_z_i = --- NO BODY DEFINED: ADD YOUR CODE HERE.--- ;
endReplace the body of the function with the following code:
function[std_z_i] = fun_182682__03_function_emptybody(std_x,std_y)
std_z_i(1) = std_x + std_y;
std_z_i(2) = std_x - std_y;
std_z_i(3) = std_x / std_y;
std_z_i(4) = std_x * std_y;
endThis simulation is available with ID 182684 with variable specification 182685. The solution for the iteration variable is also given in Table 1.
| Name | Description | Value / Initial guess | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter determining the sum of | 18.0 | ||
| Parameter | 4.0 | ||
| First component of | 6.0 | ||
| Second component of | 2.0 | ||
| Third component of | 2.0 | ||
| Fouth component of | 8.0 | ||
| Iteration variable | 10.0 | 2.0 | |
